
Simulation and Medical Education
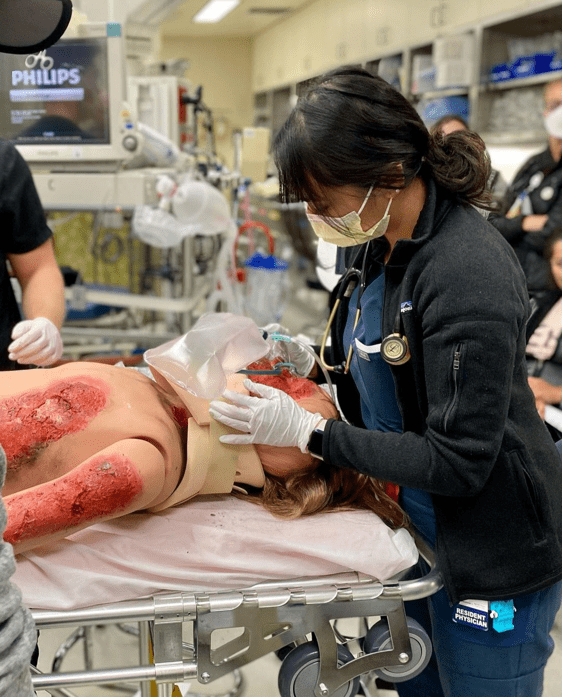 Medical education has undergone significant changes during the last decades.
One of the ways to enhance clinical competence is through Medical Simulation
training. The training has been proven to have many advantages which help
improve medical practitioners’ competencies, and in return, improve
patient safety and reduce healthcare costs.
Medical education has undergone significant changes during the last decades.
One of the ways to enhance clinical competence is through Medical Simulation
training. The training has been proven to have many advantages which help
improve medical practitioners’ competencies, and in return, improve
patient safety and reduce healthcare costs.
Medical simulation allows the acquisition of clinical skills through hands-on practice rather than an apprentice style of learning. With the recent advancements in technology, simulation tools serve as an alternative to real patients, which allows trainees to perform procedural mistakes and learn from them without the fear of harming the patient.
While hands-on learning with real patients cannot be completely replaced, simulation training provides a safe environment for learning. Making mistakes can be a valuable part of the learning process. In the simulation environment, patients are not put at risk.
In response to the effectiveness of simulations, the ACGME has strongly suggested and, in some cases, mandated the incorporation of this type of training into the curriculum of many residency programs. Additionally, many medical schools, nursing schools and paramedic schools have begun to introduce simulation into their pre-graduate training, which is reflected in the expectations of new incoming trainees, who look for the simulation capabilities of the proposed hiring institution.